Antique Comedians of Malidinesia would like to play a new discovered
comedy of Aristofanes. Putting it on a stage should be a big surprise for
the audience so all the preparations must be kept absolutely secret.
The ACM director suspects one of his competitors of reading his
correspondece. To prevent other companies from revealing his secret, he
decided to use a substitution cipher in all the letters mentioning the
new play.
Substitution cipher is defined by a substitution table assigning each
character of the substitution alphabet another character of the same alphabet.
The assignment is a bijection (to each character exactly
one character is assigned - not neccessary different).
The director is afraid of disclosing the substitution table and
therefore he changes it frequently. After each change he chooses a few
words from a dictionary by random, encrypts them and sends them together with
an encrypted message. The plain (i.e. non-encrypted) words
are sent by a secure channel, not by mail. The recipient of the message
can then compare plain and encrypted words and create
a new substitution table.
Unfortunately, one of the ACM cipher specialists have found that this
system is sometimes insecure. Some messages can be decrypted by the rival
company even without knowing the plain words. The reason is
that when the director chooses the words from the dictionary and encrypts them,
he never changes their order (the words in the dictionary are
lexicographically sorted). String
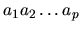 is lexicografically smaller than
is lexicografically smaller than
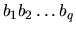 if there exists an integer i,
if there exists an integer i,
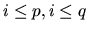 ,
such that aj=bj for each j,
,
such that aj=bj for each j,
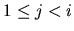 and ai < bi.
and ai < bi.
The director is interested in which of his messages could be
read by the rival company. You are to write a program to determine that.
The input consists of N cases. The first line of the input
contains only positive integer N. Then follow the cases.
The first line of each case contains only two positive integers
A,
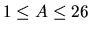 ,
and K, separated by
space. A determines the size of the substitution alphabet (the
substitution alphabet consists of the first A lowercase letters
of the english alphabet (a-z) and K is the number of encrypted
words. The plain words contain only the letters of the substitution
alphabet. The plain message can contain any symbol, but only the letters of
the substitution alphabet are encrypted. Then follow K lines,
each containing exactly one encrypted word. At the next line is encrypted
message.
,
and K, separated by
space. A determines the size of the substitution alphabet (the
substitution alphabet consists of the first A lowercase letters
of the english alphabet (a-z) and K is the number of encrypted
words. The plain words contain only the letters of the substitution
alphabet. The plain message can contain any symbol, but only the letters of
the substitution alphabet are encrypted. Then follow K lines,
each containing exactly one encrypted word. At the next line is encrypted
message.
For each case, print exactly one line. If it is possible
to decrypt the message uniquely, print the
decrypted message. Otherwise, print the sentence
`Message cannot be decrypted.'.
2
5 6
cebdbac
cac
ecd
dca
aba
bac
cedab
4 4
cca
cad
aac
bca
bdac
abcde
Message cannot be decrypted.
Miguel A. Revilla
2000-02-15